EGG PRO 90+ 1KG
EGG PRO 90+ 1KG
🚫 Lactose Free
🥚 Zero Carbs and Fats
🍍 Enhanced with bromelain
Note: Only 7 units left in stock
Couldn't load pickup availability
- 7-10 Day Shipping
- 30-Day Guarantee
- 24/7 Chat Support
Is Egg Pro 90+ lactose-free?
Is Egg Pro 90+ lactose-free?
Yes!
Since it's made entirely from eggs, this protein powder is completely lactose-free...
Making it a great option for anyone with dairy sensitivities.
How does Egg Pro 90+ compare to whey protein?
How does Egg Pro 90+ compare to whey protein?
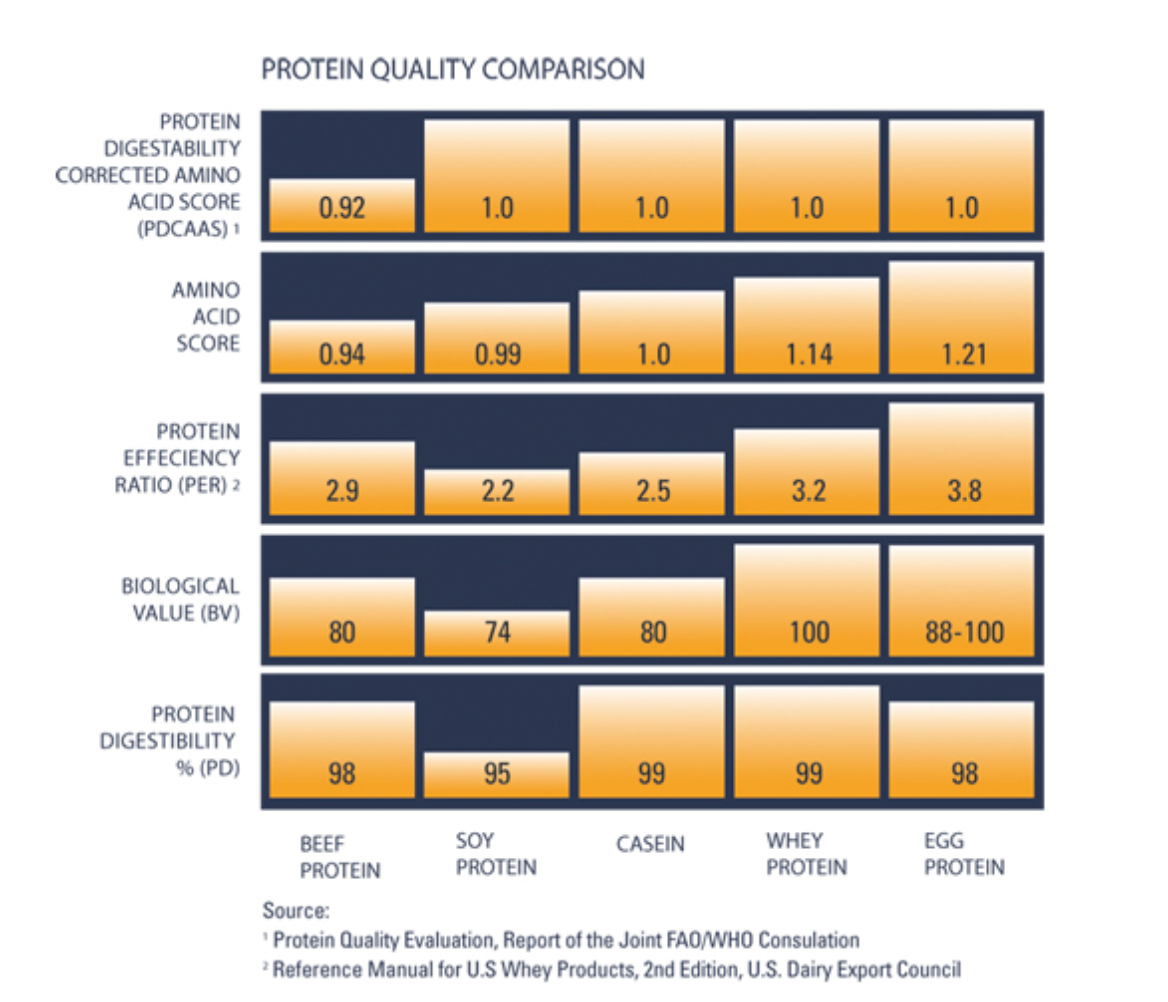
Egg protein has a higher percentage of protein per serving compared to most whey concentrates.
It’s also lower in calories, carbs, and fats, making it ideal for those on strict diets.
Are there any side effects?
Are there any side effects?
Creatine is generally safe when taken as directed.
Some people may experience mild stomach discomfort, but this is rare.
Stay hydrated and follow the dosage instructions for best results.
Egg protein powder Vs Whey protein?
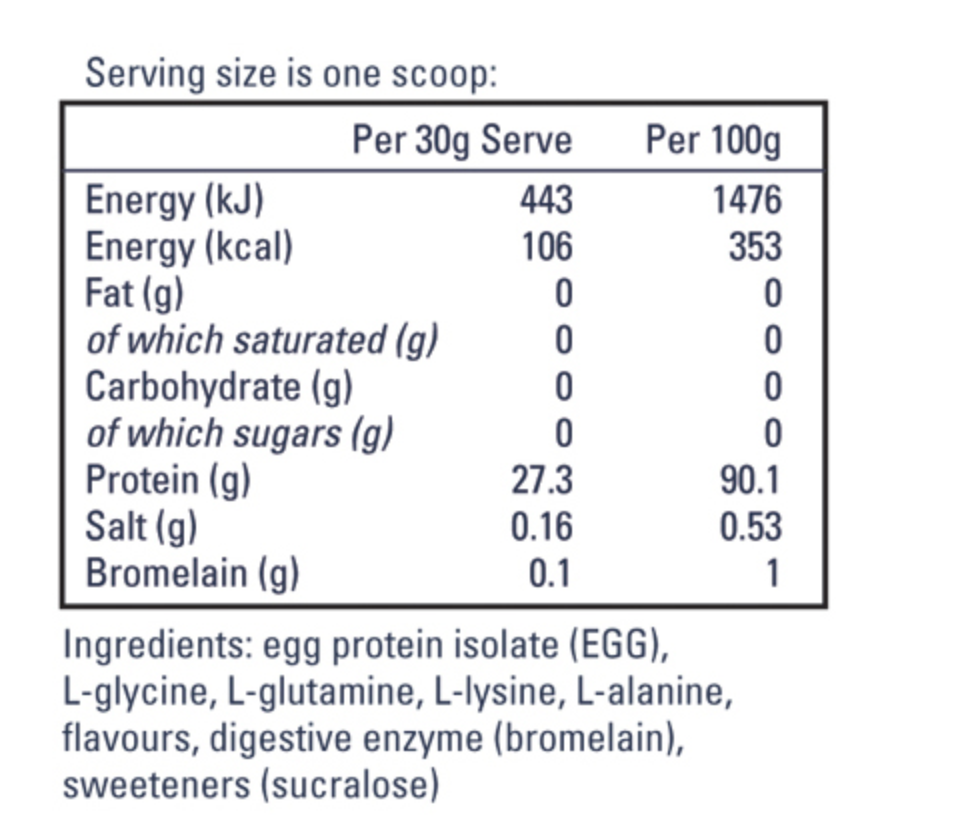
Nutritionally, egg protein powder and whey are fairly similar. Both contain all 9 essential amino acids that your body needs and cannot make itself. This means they are both complete proteins sources.
The % per serve is on average higher as most whey protein supplements contain whey concentrate which has a lower % protein due to the addition of carbs and fat. Egg protein contains ZERO carbs and ZERO fat. which leaves more room for higher % protein per 100g. As a result egg protein is also lower in calories per serve compared to whey.
Egg protein % per 100g is comparable to whey isolate or hydrolysed isolate, however is more economically affordable.
Is egg protein lactose free?
The biggest issue with users of whey protein is the reaction to the lactose from milk, where whey comes from. Though whey isolate may claim to contain little to no lactose, some users may experience feeling very full or even bloated. Egg protein is derived entirely from eggs, so the only issue that may arise could be from people who are allergic to eggs.
How much protein do we need per day?
Protein is unlike other micronutrients that are determined by age and gender. With protein it’s body weight that matters. The original RDA (Recommended Dietary Allowance) of 0.8 g/kg of body weight per day equals an “adequate” 46g for a 57kg woman and 56g for a 70kg man.
However, research shows that “adequate” isn’t the same as “optimal.” RDA defined adequate as the level of protein required to offset deficiency in 98% of people. This is not the amount required to help maintain or build muscle mass. Sports nutritionist’s collective body of evidence indicates 1.5 -1.7g per kg lean bodyweight for resistance training-induced gains in muscle mass and strength.
Is protein supplementation required?
Adults lose about 3% to 8% of muscle mass per decade after age 30. This rate increases even more after age 60. To counter this loss, an appropriate physical activity and optimal protein intake is important to preserve muscle mass. This also will prevent age-related decline in health and physical function. This is especially important in older adults, needing more protein to stimulate muscle synthesis.
Does age affect digestion?
As a normal part of the aging process, natural digestive enzyme production begins to decline from the age of 27. With age these organs function become impaired, resulting
in: bloating, gas, indigestion, abdominal pain, and other digestive malfunctions. With fewer digestive enzymes, improper digested food causes uncomfortable symptoms. Some elderly can even become malnourished from poor absorption.
Age also decreases lactase levels, leading to intolerance of dairy products by many older adults (lactose intolerance). So switching to a non dairy based protein source may actually improve quality of life.
What is bromelain?
Bromelain is a mixture of enzymes found naturally in the juice and stems of the pineapple plant (Ananas comosus). It is a form of proteases, which break down protein into its building blocks, including amino acids.